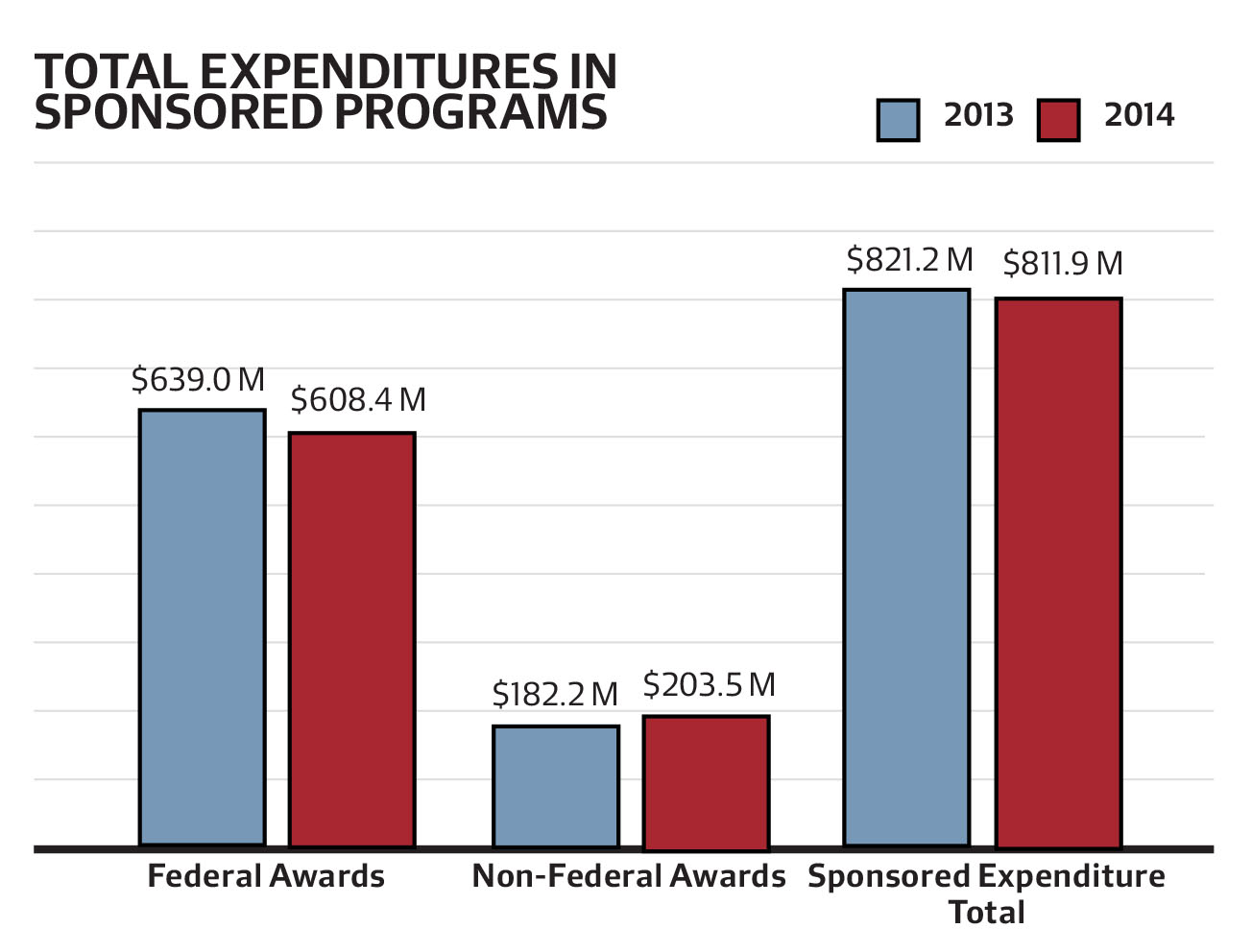
The Harvard Research Funding Crisis has sent shockwaves through both educational and scientific communities, as researchers scramble to adapt to a sudden funding freeze that has halted significant projects. With over $2.2 billion in research funds frozen, professors like Don Ingber, the director of the Wyss Institute, face the grim reality of paused innovations such as organ-on-a-chip technology that have the potential to redefine our understanding of biology and medicine. This crisis not only threatens groundbreaking academic research but also jeopardizes the very foundation of American innovation, which thrives on collaboration between academia and government. As talented researchers reconsider their futures, the academic research impact of this funding halt could resonate for years, stifling progress and deterring international scientists from contributing to Harvard’s legacy. The looming question remains: how will institutions like Harvard navigate the complex landscape of research funding while upholding their commitment to scientific advancement?
A significant setback in financial support for research initiatives at prestigious universities, particularly at Harvard, is currently reverberating across the academic landscape. This unexpected funding freeze, which has affected numerous vital projects, poses a serious threat to academic research and innovation within the institution. Researchers such as Don Ingber are particularly impacted, as they work on pioneering technologies that could revolutionize healthcare, including cutting-edge organ-on-a-chip systems designed for crucial studies. The crisis underscores a larger conversation about the sustainability of research funding and its implications for America’s innovation ecosystem. As the situation unfolds, the ripple effects may hinder not just ongoing experiments, but also long-term scholarly pursuits that drive advancements across various fields.
The Harvard Research Funding Crisis: Implications for Innovation
The recent Harvard research funding crisis marks a significant turning point for academic innovation in the United States. With a freeze of approximately $2.2 billion in research funding, essential projects that drive academic advancements and technological breakthroughs are at risk. This stoppage, especially affecting projects like those led by Don Ingber at the Wyss Institute, creates not just an obstacle in scientific inquiry but poses a tangible threat to the innovation ecosystem that has been built over decades. The implications go far beyond immediate research stoppages; they ripple through the academic community affecting students, postdoctoral fellows, and the broader industry that relies on fresh scientific knowledge and innovation.
In this context, organ-on-a-chip technology, a focus of Ingber’s work, illustrates the critical nature of funded research. This groundbreaking technology is not only vital for understanding human biology in various environments, such as space and environments affected by nuclear exposure, but it also showcases potential advancements in pharmaceuticals and injectable therapies. The impact of this funding halt on their progress could mean losing valuable insights and delaying life-saving innovations, thereby stifling the very core of scientific development that underpins America’s economy and future advancements.
Innovative Solutions Amidst Research Funding Challenges
Amid the challenges posed by the funding freeze, innovative solutions are paramount for researchers facing uncertainty. Don Ingber’s strategy illustrates a proactive approach to mitigate the effects of halted projects at the Wyss Institute. By reallocating personnel to other grants and seeking internal funding, Ingber aims to retain his talented team and ensure their valuable contributions do not go to waste. This adaptability not only safeguards the researchers’ careers but also embodies the spirit of innovation that is critical to overcoming obstacles. In academic settings, maintaining the continuity of research is vital, as interrupted projects can lead to the loss of momentum and essential findings.
Furthermore, the pressure to innovate under dire constraints can lead to new collaborative efforts, as researchers may find ways to share resources or expertise across the university. The synergy created through these collaborations can foster a more resilient research culture, emphasizing shared goals that strengthen academic inquiry. Ingber’s efforts to protect his team while continuing to advocate for the importance of funding underscore how innovation is propelled during times of crisis, needing both creativity and collaboration to maintain America’s standing in research and technology.
The Role of Government in Academic Research Funding
The current freeze in research funding sparks a significant discussion about the role of government in supporting academic research. Historically, partnerships between governmental bodies and academic institutions have been foundational to the nurturing and development of groundbreaking technologies. Innovations such as organ-on-a-chip have emerged from such collaborations, demonstrating the vital importance of sustained investment in scientific inquiry. By prioritizing research funding, the government not only fuels advancements in technology but also addresses critical challenges facing society, from healthcare to environmental safety. However, the recent funding freeze poses pressing questions regarding how governmental policies will continue to foster such partnerships and lead to beneficial outcomes.
Without adequate funding, the path of innovation becomes fraught with challenges that can stall research and development cycles. Don Ingber articulated the concern that significant advancements crucial for public health, space exploration, and energy sustainability could face setbacks. The intertwining of academia and government efforts in research showcases how such funding supports diverse fields, enhancing everything from cancer therapies to technological developments that meet emerging global needs. As the pressure mounts, it is essential for stakeholders to advocate for renewed support and find solutions to stabilize funding and protect the future of research.
Impact of Funding Cuts on Global Collaboration in Science
The interruption in research funding at Harvard also has profound implications for global scientific collaboration. Institutions around the world look to American universities like Harvard as leaders in innovative research and discovery. The recent funding crisis has raised crucial alarms among international researchers who consider the U.S. as a hub for academic advancements. The potential loss of talent as scientists contemplate opportunities abroad could result in a significant brain drain, negatively affecting the collaborative environment that has long flourished within American academia. In this context, having renowned projects like Ingber’s organ-on-a-chip could become less attractive to international researchers due to uncertainty about the stability of support.
As the global scientific community pivots towards collaboration on pressing issues such as climate change, healthcare innovations, and space exploration, the repercussions of reduced research funding become particularly pronounced. The prospects for future partnerships hinge on the ability of U.S. institutions to remain competitive and attractive destinations for researchers worldwide. The fear among prospective scientists about the stability of their positions in the U.S., particularly given the current climate, could deter skilled individuals from collaborating on crucial research efforts that benefit humanity as a whole.
Innovations in Organ-on-a-Chip Technology: A Future at Risk
Organ-on-a-chip technology exemplifies how cutting-edge research has the potential to revolutionize medicine and pharmaceuticals. Developed at the Wyss Institute, this technology offers unprecedented insights into human physiology and disease modeling by replicating organ systems on microchips. Don Ingber’s current research delves into the effects of radiation damage on organs, translating into potential solutions for ailments related to cancer treatments and environmental hazards. However, the immediate halt in funding has placed an enormous burden on the continuity of such transformative projects, jeopardizing not only the momentum of ongoing studies but also the potential breakthroughs that can stem from them.
In today’s fast-paced scientific environment, the ability to conduct research without interruption is crucial. Organ-on-a-chip research particularly requires sustained effort to capture longitudinal data and validate results before they can impact clinical applications. The cessation of funding means researchers must halt their experiments, effectively pausing scientific progress and allowing competitors, both domestic and international, to overtake in pivotal areas of study. The future of innovations arising from organ-on-a-chip technology hangs in the balance, emphasizing the urgent need for a reinstatement of funding and support for vital research initiatives.
Academic Research Impact: The Need for Sustainable Change
The impact of academic research extends beyond the laboratory, contributing significantly to economic and societal advancements. As seen in the current crisis at Harvard, the link between research funding and innovation has never been more profound. Don Ingber’s warnings about the potential stagnation of academic contributions underscore a vital truth; without sustainable funding mechanisms, the very foundation of American innovation is at risk. As a leader in the field, Ingber emphasizes not only the contributions of his own projects but also the wealth of knowledge that can emerge from a thriving academic research landscape. This moment calls for a reevaluation of how research is funded and supported.
In recognizing the integral role of research in driving technological advancements, stakeholders must prioritize sustainable changes to the funding landscape. This includes a strategic partnership between universities, government, and industry to ensure the stability that researchers need to pursue their work with confidence. The lessons drawn from this funding crisis at Harvard must serve as a turning point to advocate for more resilient research funding structures that can withstand political fluctuations, thereby preserving the academic research impact that serves society at large.
Future Prospects of Harvard’s Innovations in Technology
Looking toward the future, Harvard’s innovations, particularly in the fields of medicine and technology, face a tumultuous path ahead amidst current funding aids. Projects like the organ-on-a-chip developing insights into gastrointestinal health and other critical healthcare applications emphasize the necessity of robust funding to catalyze innovation that directly impacts human well-being. The looming uncertainty resulting from funding crises requires that stakeholders find creative solutions to secure the future of such programs. As advocates for scientific progress, researchers like Ingber illustrate the urgency that accompanies these projects, as they not only drive academic research but also outline the promise of future health technologies.
However, translating innovation into application requires not just a resurgence of inspiration but also uncompromised support. Collaborations extending across universities, government institutions, and private sectors would create an ecosystem that nurtures sustainable development of groundbreaking technologies. As Ingber points out, the essence of American innovation has thrived on partnerships that promote technological advancement and share knowledge. Thus, robust support for research and development is paramount to ensuring that the promise of Harvard’s technological innovations continues to shape the future of healthcare and other vital sectors.
The Cultural and Economic Impact of Research Funding on Innovation
The intersection of culture and economics in research funding underscores the broad impact that academic institutions have on fostering innovation. Harvard has long served as a beacon in cultivating talent and pioneering new technologies; however, the current funding freeze threatens to destabilize this role. This situation excludes budding researchers from engaging in essential studies, creating a sense of disheartenment and instability—especially for international talent considering the U.S. for their academic careers. Ingber’s accounts highlight how this funding crisis has already caused scholars to reconsider their positions, potentially altering the landscape of American scientific research for years to come.
Furthermore, the long-term effects on the economy can be substantial: as innovation slows, so does the development of new technologies that have historically driven economic growth. The partnership between research institutions and government funding has been the backbone of advances that impact everything from tech industries to public health. Ensuring continued investment in academic research is critical for stimulating economic growth and maintaining America’s status as a leader in innovation. Each halted project represents not just a loss of potential discoveries but also a broader cultural shift that could deter future generations from pursuing careers in science and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Harvard Research Funding Crisis and its implications for academics?
The Harvard Research Funding Crisis refers to the freeze on approximately $2.2 billion in research funding at Harvard University, notably impacting significant projects like those at the Wyss Institute by Don Ingber. This crisis has raised concerns about the future of academic research and innovation in the U.S. It not only halts ongoing projects but also affects talented researchers, hampering progress in critical fields such as organ-on-a-chip technology.
How has organ-on-a-chip technology been affected by the funding freeze at Harvard?
The organ-on-a-chip technology projects at Harvard, led by Don Ingber, faced a stop-work order due to the Harvard Research Funding Crisis. These projects, vital for understanding human responses to radiation and microgravity, are now halted, jeopardizing advancements in medical research and the potential to model human organ damage effectively.
Who is Don Ingber and what role does he play in the Harvard Research Funding Crisis?
Don Ingber is the founding director of the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard. He has been a key figure during the Harvard Research Funding Crisis, managing the impact of the funding freeze on critical projects, including those utilizing organ-on-a-chip technology. His work aims to maintain research continuity and address urgent challenges in academic innovation.
What are the potential consequences of the Harvard Research Funding Crisis on innovation in America?
The Harvard Research Funding Crisis threatens to undermine the collaborative relationship between government and academia that has driven American innovation for decades. With the freeze on vital funding, projects that contribute to technological advancements, such as those utilizing organ-on-a-chip technology, may stall, resulting in a significant setback for scientific research and the broader economy.
How does the funding freeze affect the academic research environment at Harvard?
The funding freeze has created an environment of uncertainty and fear among researchers at Harvard, including project halts and the urgent need for reallocating staff. With critical projects paused, the Harvard Research Funding Crisis poses a risk to the university’s ability to attract and retain top talent, ultimately hindering the academic research landscape.
What legal actions has Harvard taken regarding the research funding freeze?
In response to the research funding freeze imposed by the federal government, Harvard filed a lawsuit declaring the demands behind the freeze as illegal and unconstitutional. This legal action is part of the university’s efforts to restore funding and protect the integrity of academic research during the Harvard Research Funding Crisis.
What are the implications of the funding crises on future collaborations in research?
The Harvard Research Funding Crisis may deter both domestic and international researchers from pursuing opportunities at Harvard, affecting future collaborations essential for advancing science and technology. The uncertainty caused by the funding freeze could lead to a loss of global talent, impacting innovation and research breakthroughs across various disciplines.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Stop-Work Order | Harvard received a stop-work order targeting key research projects, leading to immediate funding and operation halts. |
| Federal Funding Freeze | Approximately $2.2 billion in research funding was frozen by the U.S. government, impacting several university projects. |
| Lawsuit Against the Government | Harvard filed a lawsuit declaring the government’s demands for changes as unconstitutional, while seeking to restore funding. |
| Impact on Researchers | Researchers faced uncertainty regarding project viability, job security, and the continuation of critical research. |
| Importance of Research Projects | Key projects like organ-on-a-chip technologies are vital for understanding radiation damage and astronaut health in space missions. |
| Fear Among Scientists | Many scientists, including international researchers, are reconsidering their tenure at Harvard due to the instability in funding and policy. |
| Innovation Crisis | This situation threatens the foundation of America’s innovation economy and its partnership with academia. |
Summary
The Harvard Research Funding Crisis has revealed significant challenges within academic institutions as they face abrupt halts in vital research due to federal funding freezes and bureaucratic disputes. With ongoing lawsuits and a palpable sense of uncertainty among researchers, the stability of America’s innovation economy hangs in the balance. This crisis underscores the pressing need for sustained investment in academia and research to foster innovation and maintain the country’s position as a leader in scientific advancement.